West Virginia recently changed its homeschool participation reporting requirement from annually to one time.
History
West Virginia, in the southern United States, legalized homeschooling in 1987. In this state, homeschooling is not considered private schooling.
Regulation
There are several options for homeschooling in West Virginia. The state requires parents who homeschool their children, ages 6 to 17, to provide a one-time notice to the county superintendent. The state law also requires parents to ensure that the instruction time is equal to that of public schools: 180 instructional days per term. Homeschooled students must also receive instruction in the core subjects of reading, language, mathematics, science, and social studies.
Parents who direct their children’s education at home must have at least a high school diploma or GED and provide a copy to the county superintendent. Homeschooled students must do one of the following: take an annual standardized assessment in reading, language arts, math, science, and social studies; take a state assessment; provide a portfolio of work reviewed by a certified teacher; or submit an alternative assessment approved by both parties.
Homeschooled students have limited access to courses and other offerings at local public schools. For example, they may request access to any course, but the county board must approve attendance. They are also eligible for interscholastic sports participation with some requirements. For example, it appears that they must enroll in at least a virtual class at the public school. Access to SPED services appears limited to students who have fallen behind for three consecutive years. Services for other students with special needs are unclear.
State Data
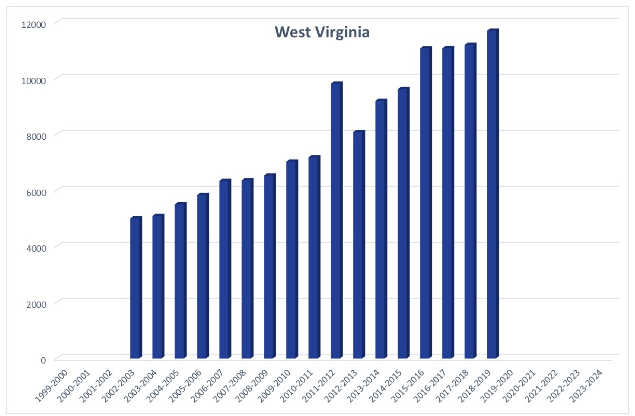
West Virginia used to require parents to report annually. As a result, the state had many years of longitudinal homeschool participation data that it publicly reported. However, the state changed its requirements and now asks parents to report only when they begin to homeschool. Therefore, participation data are available through 2019. Historically, there were about 5,000 homeschooled students in the early 2000s. Just before the pandemic, there were nearly 12,000.
U.S. Census estimates indicate that around 5.4% of West Virginia families homeschooled in the spring of 2020 and increased to 16.6% by the fall of 2020. This was higher than the national estimate of 11.1% at this time. Based on U.S. Census data, our calculations indicate that about 8.89% of K-12 students in (state) were homeschooled during the 2022-23 school year, and 8.23% during the 2023-24 school year. Due to survey changes, the data from 2020 reflects the percentage of households, while the data from following years reflects the percentage of students.
Cross-Sector Comparison
We cannot calculate a cross-sector comparison because we lack information on homeschool participation.
School Choice Context
In addition to homeschooling, parents in West Virginia have various educational choices available. These options include open enrollment in traditional public schools through inter- and intra-district choice. West Virginia does not have any charter or magnet schools. The state recently passed one of the nation’s most expansive educational savings accounts. Homeschooled students are only eligible if they meet the age/grade or prior public school attendance requirement, but all students will be eligible in 2026.
Commentary
West Virginia holds homeschooled students to a higher testing standard than public school students. The West Virginia state test, given in grades 3-8, only covers English language arts, math, and science. Homeschooled students have to take a civics test unless they opt for the state test. Further, the state test is not nationally normed, meaning the results are comparable to other students of similar ages across the country.

-
16.6% Families
Around 16.6% of families in West Virginia homeschooled during the height of the pandemic (Fall 2020).
-
1987 Legalized
Homeschooling was legalized in 1987 in the state of West Virginia.
-

-
More Information
16.6% Families
Around 16.6% of families in West Virginia homeschooled during the height of the pandemic (Fall 2020).
1987 Legalized
Homeschooling was legalized in 1987 in the state of West Virginia.

More Information
Last updated March 2025.