Ohio has a few homeschool options, including traditional homeschooling or schooling from home as a nonchartered and non-tax-supported school.
History
Ohio, located in the midwestern United States, legalized homeschooling in 1989. The homeschool laws were codified in the Ohio administrative code as OAC 3301-34.
Regulation
While Ohio offers parents a few options for homeschooling, this summary focuses on traditional homeschooling. In Ohio, homeschooling should be directed “primarily” by the parent or legal guardian. Ohio parents who homeschool their children, ages 6 to 18, must notify their local school superintendent with the student’s name and contact information and an assurance that certain subjects will be taught, except where in conflict with religious beliefs. With the passage of House Bill 33 in 2023, the state no longer requires parents to provide annual student assessment, though it does still require annual notification. This bill also removed instructor education requirements, as well as requirements for a minimum number of hours of instruction or for parents to maintain records. Homeschool students are required to receive instruction in certain subject areas.
Ohio’s subject requirements look very similar to Pennsylvania’s and require a broad array of subject instruction. Specifically, Ohio homeschooled students must receive instruction in English language arts, mathematics, science, history, government, and social studies. Homeschooled students may participate in the statewide assessments free of charge.
Homeschooled students may join extracurricular activities at their local public schools. However, this access is restricted to extracurriculars and sports only, is unfunded, and does not extend to other nonpublic students. Students may take courses at the district’s discretion. It is unclear if homeschooled students with special needs are eligible for services through their local public school.
State Data
Ohio publicly reports homeschool participation data starting in 2005. For example, around 23,000 students reported homeschooling in 2010, which increased to over 50,000 at the height of the pandemic. District-level information is also available.
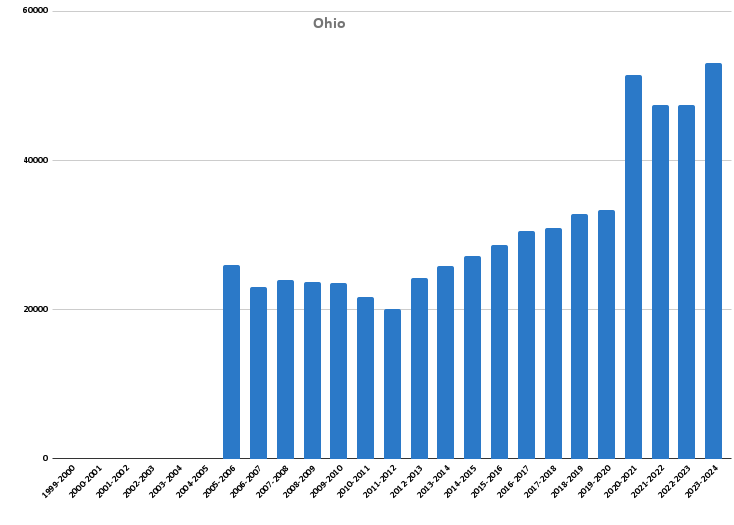
Similarly, U.S. Census estimates indicate that around 6.1% of families homeschooled in the spring of 2020 and increased to 9.4% by the fall of 2020. This compares to the national average of 11.1% at the time. Based on U.S. Census data, our calculations indicate that about 5.25% of K-12 students in Ohio were homeschooled during the 2022-23 school year, and 5.68% during the 2023-24 school year. Due to survey changes, the data from 2020 reflects the percentage of households, while the data from following years reflects the percentage of students.
Cross-Sector Comparison
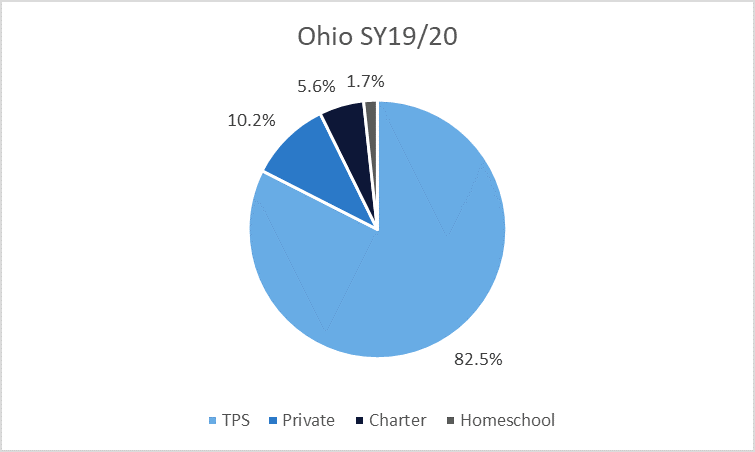
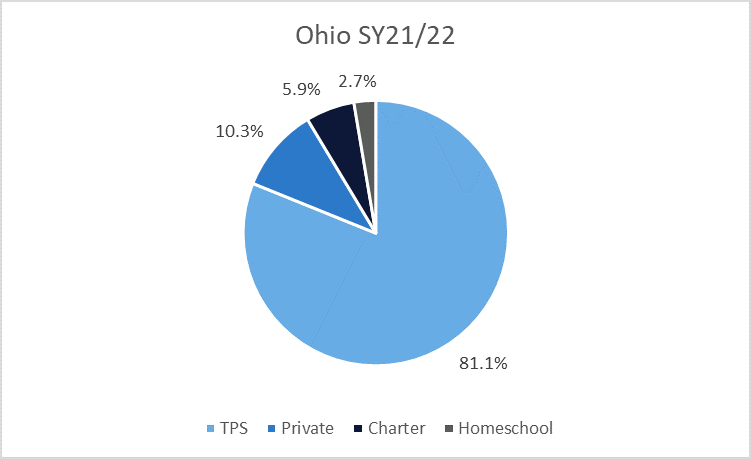
During the 2019-20 academic year, 1.7% of Ohio’s K-12 students were homeschooled. Homeschool participation in the state was much lower than the 10.2% of private school students. Charter school participation was also lower than private school participation in Ohio, at 5.6%. In 2021-22, 2.7% of Ohio’s K-12 students were homeschooled, 10.3% of students attended private schools. Charter school participation was 5.9%.
School Choice Context
In addition to homeschooling, parents in Ohio have broad educational choices available. These options include traditional public schools with inter- and intra-district choice, magnet and charter schools, and multiple private school choices, including some aimed at homeschooled families. The K-12 Home Education Tax Credit, launched in 2021, provides all homeschooled families with a $250 tax credit.
Commentary
The mandatory subject requirements in Ohio are robust. This is another case where homeschooled students and parents may be held to a higher standard than public school peers. However, Ohio offers homeschool families free testing, access to public school experiences, and a tax credit.

-
9.4% Tax Credit
Around 9.4% of families in Ohio homeschooled during the height of the pandemic (Fall 2020).
-
1989 Legalized
Homeschooling was legalized in 1989 in the state of Ohio.
-

9.4% Tax Credit
Around 9.4% of families in Ohio homeschooled during the height of the pandemic (Fall 2020).
1989 Legalized
Homeschooling was legalized in 1989 in the state of Ohio.

Last updated March 2025.