Pennsylvania is one of the only states where homeschoolers have a legal right to borrow textbooks and curriculum from their local school districts.
History
In the Northeastern United States, Pennsylvania legalized homeschooling in 1949 and updated the laws in 1988. Parents, guardians, or a person with legal custody may homeschool. The state does not define homeschooling as a form of nonpublic schooling.
Regulation
Pennsylvania offers multiple options for homeschooling students. The state requires parents who elect to homeschool their children, ages 6 to 18, to submit a notarized affidavit of intent to homeschool to the local superintendent annually. Additionally, the parent must submit an instructional plan outlining the educational objectives in each subject; proof of immunization or exemptions; and evidence that the child has received appropriate medical services.
Parents who direct their children’s education at home must have at least a high school diploma or GED. Parents may hire a “properly qualified private tutor,“ defined as a certified teacher working with a single family. A list of other requirements and provisions accompany private tutoring of homeschooled students. See here and here for more information. Also, 24 P.S. §13-1327 (a).
Pennsylvania has many requirements that address instructional time. For example, homeschooled students must attend school for at least 180 days or 900-990 hours, depending on grade level. Parents must maintain attendance records in the student’s portfolio.
Pennsylvania’s subject requirements for homeschooled students are the most extensive in the nation. For example, in the elementary grades, homeschooled students must receive instruction in “English, to include spelling, reading and writing; arithmetic; science; geography; history of the United States and Pennsylvania; civics; safety education, including regular and continuous instruction in the dangers and prevention of fires; health and physiology; physical education; music; and art.” The state requires more subjects for secondary-level homeschooled students.
However, unlike many other states, homeschool parents in Pennsylvania have the legal right to borrow textbooks and curriculum from their local school district, free of charge. 24 P.S. §13-1327.1 (f). Also, unlike other states, homeschooled students in Pennsylvania who follow the prescribed course requirements may receive a state diploma. 22 Pa Code §4.72.
The state requires homeschooled students to take assessments in grades 3, 5, and 8, and parents may chose either the state test (PSSAs/PASAs) or one of 11 other nationally normed standardized tests. Parents should keep test results in the student’s portfolio.
With the passage of Act 55 in 2022, homeschooled students can take academic, co-curricular courses, or CTE programs from the local school district of residence. According to Pennsylvania policy, homeschooled students with special needs may request special services from their local school district, but it appears that receiving services depends upon the district superintendent’s approval. 24 P.S. §13-1327 (d).
State Data
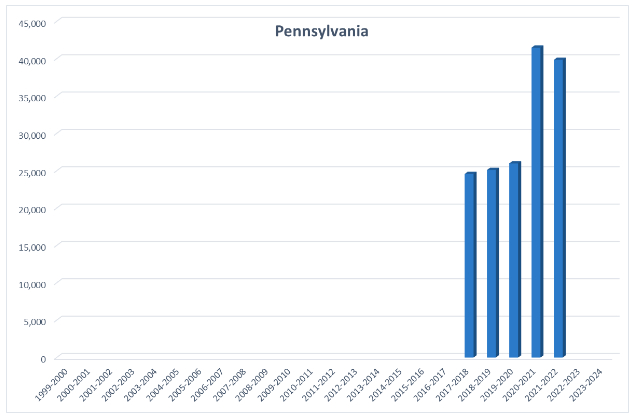
There are several years of homeschool participation data available. For example, nearly 25,000 students reported homeschooling in 2017, which increased to over 41,000 at the height of the pandemic. Pennsylvania disaggregates homeschool participation by grade, county, and district, offering more robust information on participation trends in the state.
U.S. Census estimates indicate that around 7.3% of Pennsylvania families homeschooled in the spring of 2020 and increased to 10.8% by the fall of 2020. This is comparable to the national average of 11.1% at the time. Based on U.S. Census data, our calculations indicate that about 5.57% of K-12 students in Pennsylvania were homeschooled during the 2022-23 school year, and 6.73% during the 2023-24 school year. Due to survey changes, the data from 2020 reflects the percentage of households, while the data from following years reflects the percentage of students.
Cross-Sector Comparison
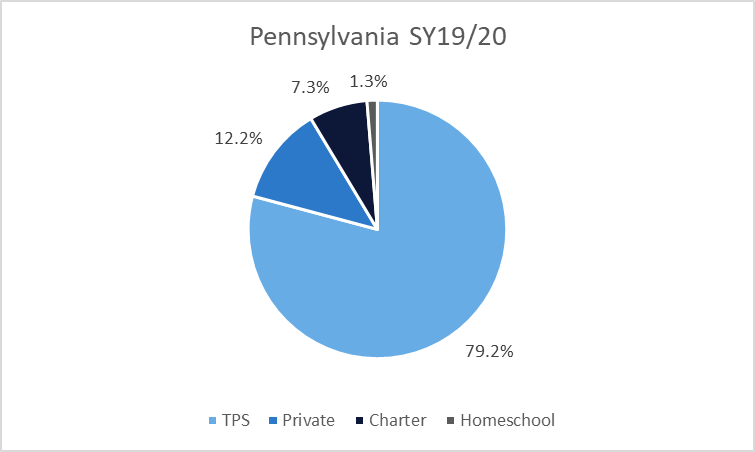
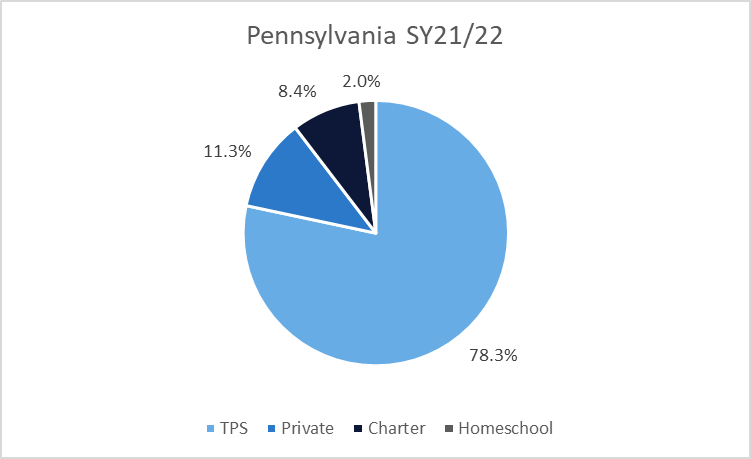
During the 2019-20 academic year, 1.3% of Pennsylvania’s K-12 students were homeschooled. Homeschool participation in the state was much lower than the 12.2% of students attending private schools and the 7.3% of students attending charter schools. In 2021-22, 2.0% of Pennsylvania’s K-12 students were homeschooled, 11.3% attended private schools, and 8.4% attended charter schools.
School Choice Context
In addition to homeschooling, parents in Pennsylvania have various educational choices available. These options include inter- and intra-district enrollment in traditional public schools, some limited charter and magnet schools, and private schools. There are also two tax credit scholarship programs, though neither of which serves homeschooled students.
Commentary
The state may hold homeschooled students and parents to a higher standard than their publicly schooled peers and teachers if publicly schooled students are not also provided instruction in the subjects required for home instruction. While the state has a considerable number of requirements, homeschooled students have broad access to services, free curricula, and an option to receive a state diploma. Few states provide these options for their homeschooled families.

-
10.8% Families
Around 10.8% of families in Pennsylvania homeschooled during the height of the pandemic (Fall 2020).
-
1949 Legalized
Homeschooling was legalized in 1949 in the state of Pennsylvania.
-

-
More Information
10.8% Families
Around 10.8% of families in Pennsylvania homeschooled during the height of the pandemic (Fall 2020).
1949 Legalized
Homeschooling was legalized in 1949 in the state of Pennsylvania.

More Information
Last updated March 2025.